Publications
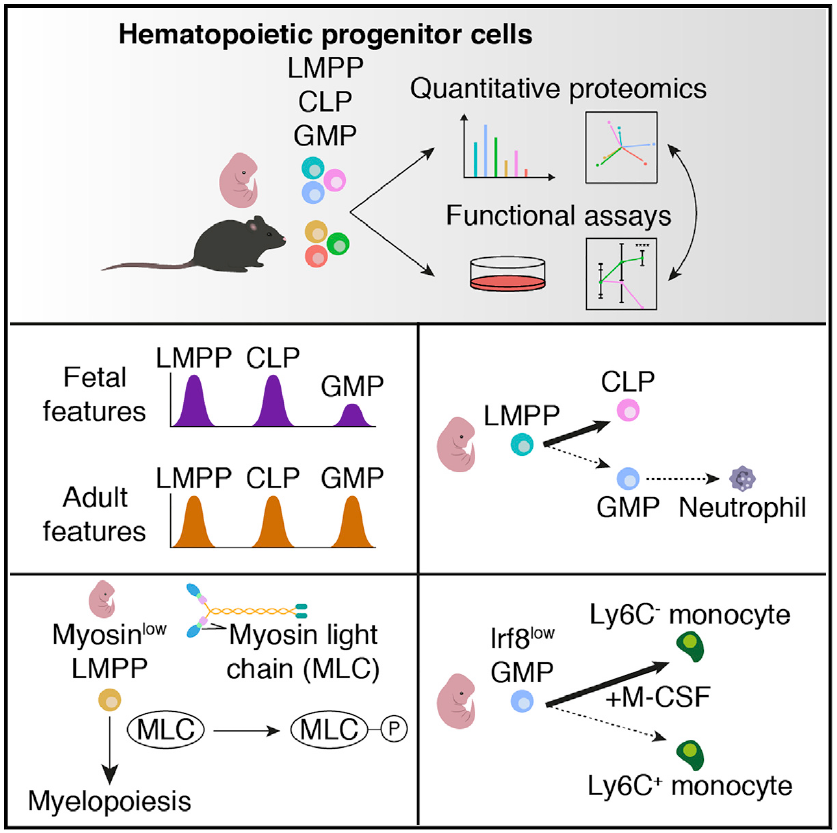
Ontogenic Shifts in Cellular Fate Are Linked to Proteotype Changes in Lineage-biased Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells
March 23, 2021 / Volume 34, Issue 23
Cell Reports
Maria Jassinskaja, Kristýna Pimková, Nejc Arh, Emil Johansson, Mina Davoudi, Carlos-Filipe Pereira, Ewa Sitnicka, Jenny Hansson
Highlights
- >4,000 proteins quantified in fetal and adult hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs)
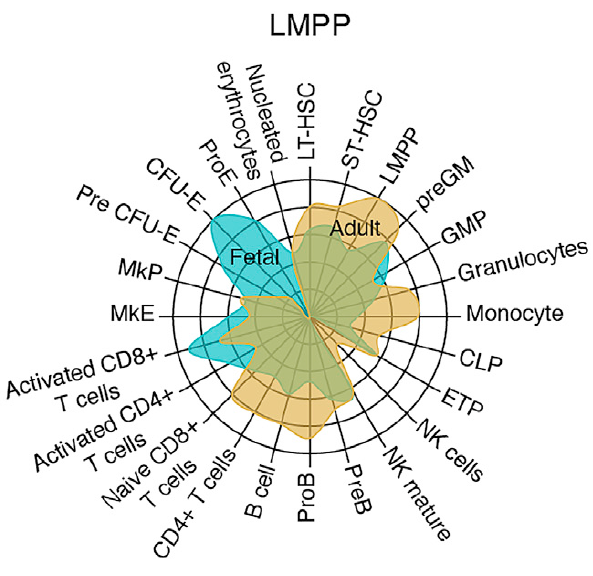
- Protein expression in HPCs separates cells based on ontogenic stage and lineage potential
- Generic fetal features are suppressed in myeloid-restricted progenitors
- Low Irf8 expression partially drives an impairment in monopoiesis in fetal HPCs
Abstract
The process of hematopoiesis is subject to substantial ontogenic remodeling that is accompanied by alterations in cellular fate during both development and disease. We combine state-of-the-art mass spectrometry with extensive functional assays to gain insight into ontogeny-specific proteomic mechanisms regulating hematopoiesis. Through deep coverage of the cellular proteome of fetal and adult lympho-myeloid multipotent progenitors (LMPPs), common lymphoid progenitors (CLPs), and granulocyte-monocyte progenitors (GMPs), we establish that features traditionally attributed to adult hematopoiesis are conserved across lymphoid and myeloid lineages, whereas generic fetal features are suppressed in GMPs. We reveal molecular and functional evidence for a diminished granulocyte differentiation capacity in fetal LMPPs and GMPs relative to their adult counterparts. Our data indicate an ontogeny-specific requirement of myosin activity for myelopoiesis in LMPPs. Finally, we uncover an ontogenic shift in the monocytic differentiation capacity of GMPs, partially driven by a differential expression of Irf8 during fetal and adult life.