Publications
Induction of a Hemogenic Program in Mouse Fibroblasts

August 1, 2013 / Volume 13, Issue 2
Cell Stem Cell
Carlos-Filipe Pereira, Betty Chang, Jiajing Qiu, Xiaohong Niu, Dmitri Papatsenko, Caroline E Hendry, Neil R Clark, Aya Nomura-Kitabayashi, Jason C Kovacic, Avi Ma'ayan, Christoph Schaniel, Ihor R Lemischka, Kateri Moore
Resources:
Highlights
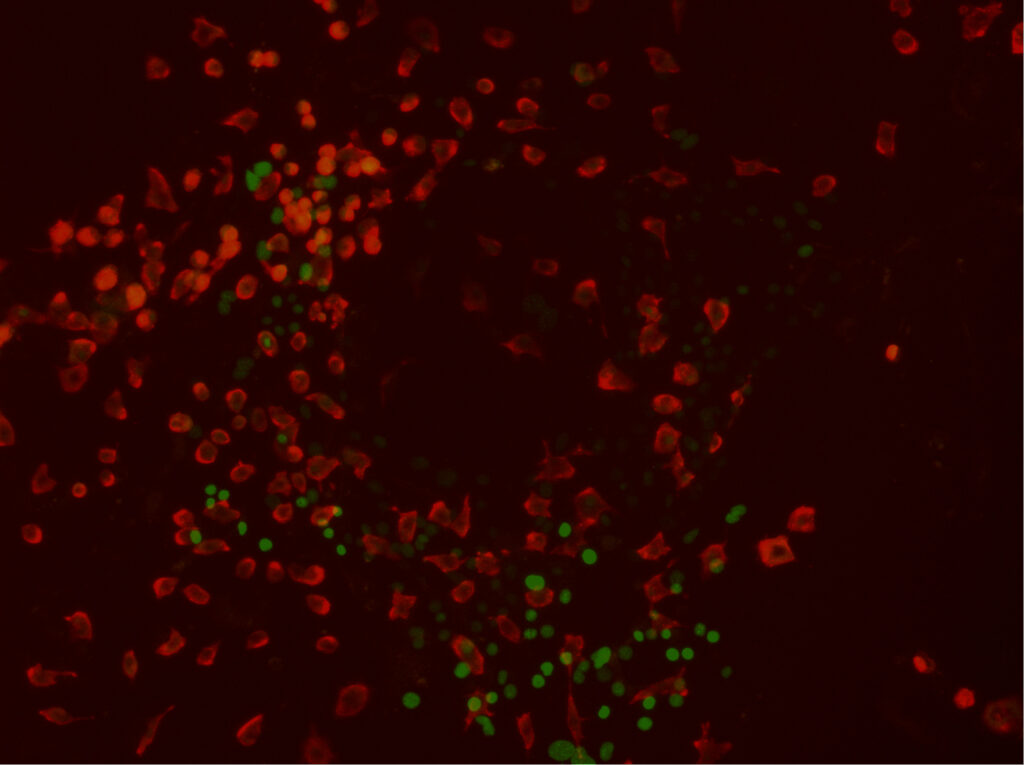
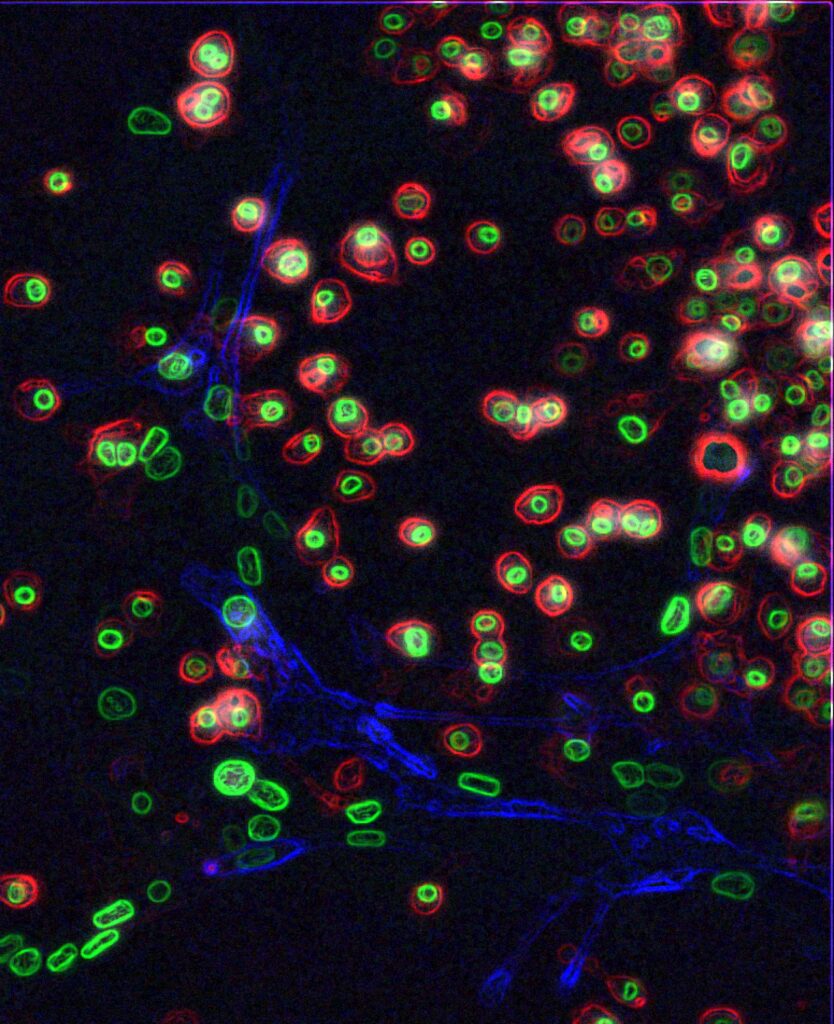
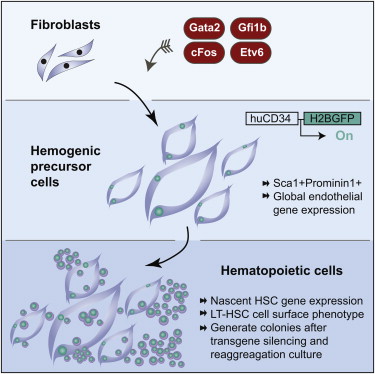
- Gata2, Gfi1b, cFos, and Etv6 induce a hemogenic program in fibroblasts
- Initial production of Sca1+Prom1+ endothelial-like precursors
- Progression to emergence of hematopoietic cells with HSC features
- Emergent cells generate colonies in vitro after reaggregation culture
Abstract
Definitive hematopoiesis emerges during embryogenesis via an endothelial-to-hematopoietic transition. We attempted to induce this process in mouse fibroblasts by screening a panel of factors for hemogenic activity. We identified a combination of four transcription factors, Gata2, Gfi1b, cFos, and Etv6, that efficiently induces endothelial-like precursor cells, with the subsequent appearance of hematopoietic cells. The precursor cells express a human CD34 reporter, Sca1, and Prominin1 within a global endothelial transcription program. Emergent hematopoietic cells possess nascent hematopoietic stem cell gene-expression profiles and cell-surface phenotypes. After transgene silencing and reaggregation culture, the specified cells generate hematopoietic colonies in vitro. Thus, we show that a simple combination of transcription factors is sufficient to induce a complex, dynamic, and multistep developmental program in vitro. These findings provide insights into the specification of definitive hemogenesis and a platform for future development of patient-specific stem and progenitor cells, as well as more-differentiated blood products.
Cover Making Of



Induced Hemogenic Cells